Localisation Platforms and Translation
Contents
Localisation Platforms and Translation¶
Localisation (l10n) and internationalisation (i18n) are important aspects in the design of any open-source project or documents. Internationalisation allows open-source project to support and satisfy the needs of multiple locales, thus “enabling” localisation, which is the adaptation of it to meet the language, cultural of a specific target locale. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) defines internationalisation (i18n) as:
“The design and development of a product, application or document content that enables easy localisation for target audiences that vary in culture, region, or language”
A Translation Management System (TMS) manages the localisation process from the beginning of a translation process until the finished product. TMS are widely used in Open source projects because they offer many advantages such as workflow, automation, transparency, and fast project delivery.
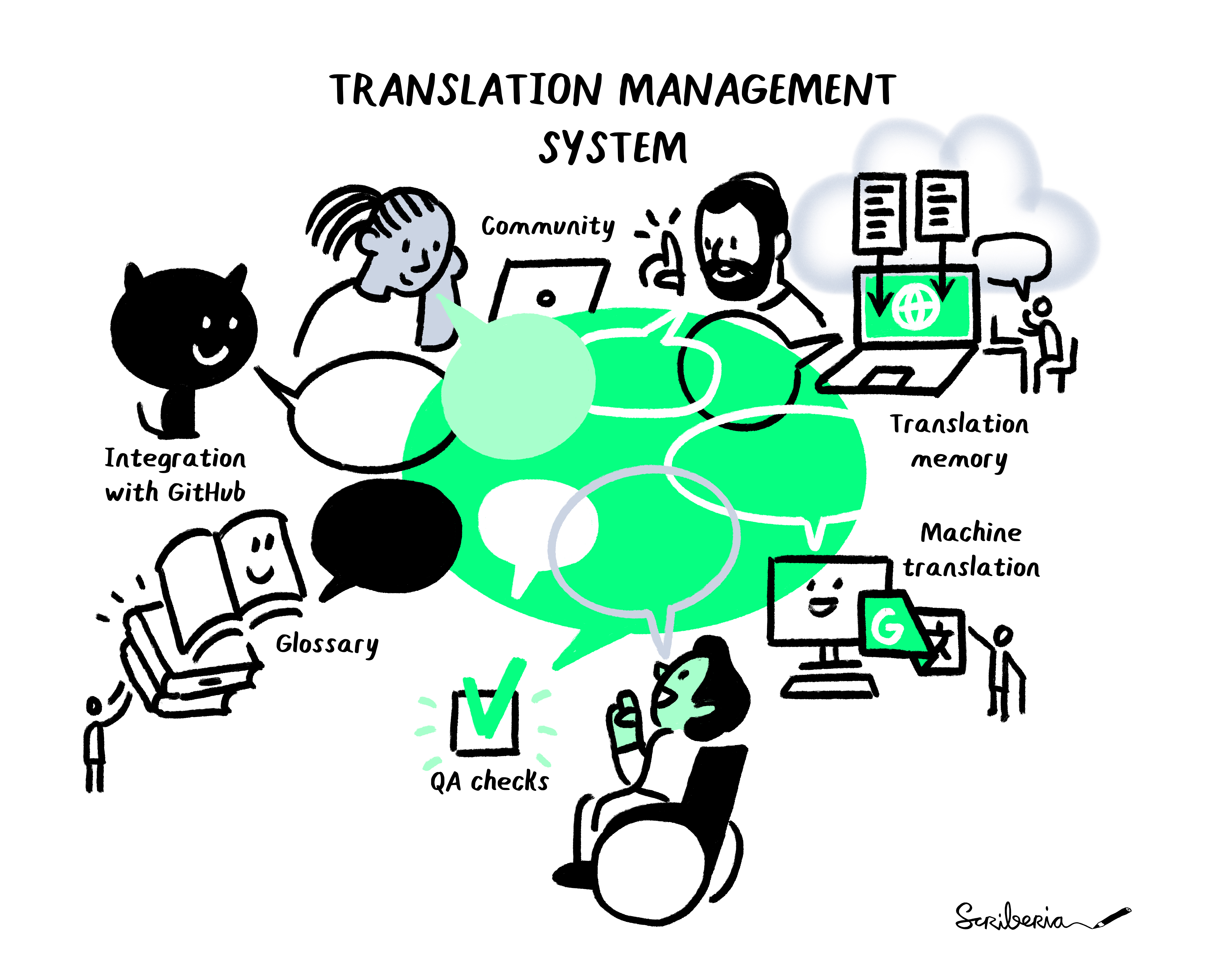
Fig. 118 The Turing Way project illustration by Scriberia. Used under a CC-BY 4.0 licence. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.3332807¶
Examples for Localisation Platforms¶
Many open source projects such as GitLab, FreeCAD, electron, PostgreSQL, OBS Studio are localised using different Translation Management System (TMS).
Features of Localisation Platforms¶
Translation Memory
Translation Memory can be described as a database of sentences or texts and their translations that can be automatically reused in/outside the project. Translation Memory can be very powerful in ensuring consistent and high-quality translations across different projects.
Glossary
A glossary is a collection of the key terms that are used in the project to ensure consistency. The glossary helps in creating, storing, and managing all the project terminology in one place.
Machine Translation
Machine Translation can speed up the translation process. It provides translation suggestions from automatic translation services like Google Translate and AutoML Translation, Microsoft Translate, and more.
Integration with GitHub
Continuous integration is vital for automation in open sources projects. Many localisation platforms offer integration with GitHub, which synchronises source and translation files between your GitHub repository and translation project.
Screenshots for the context
Screenshots provide context to the text for translation. TMS offer the opportunity of attaching screenshots to each of the phrases to provide a visual context to translators
QA checks
Many TMS support QA checks. These can include spelling and/or grammatical errors, inconsistent placeholders, and unbalanced brackets. These QA checks make the translation process smoother for translators.
In the next chapter, you’ll be introduced to Crowdin and how we use it to translate The Turing Way.
